Use Swagger to show API in Django
Document: https://drf-yasg.readthedocs.io/en/stable/readme.html#usage
A good example: https://debrajbhal.hashnode.dev/adding-custom-documentation-to-apis-in-django-rest-framework-using-drf-yasg
Add Post parameters: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50929098/django-rest-framework-how-to-add-post-parameters-to-api-documentdrf-yasg
Hard code response parameters: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62914407/drf-yasg-how-to-hide-django-rest-framework-schema
#import
from drf_yasg.utils import swagger_auto_schema
from drf_yasg import openapi
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
For GET method:
#CBV version
class TsView:
@staticmethod
@api_view(['GET']) #it depend. Add it when you choose to write CBV
@swagger_auto_schema(
operation_description="get ts info based on ts number",
responses={
200: openapi.Response("request success", schema=openapi.Schema(type=openapi.TYPE_ARRAY, items=openapi.Schema(type=openapi.TYPE_OBJECT))),
400: "request failed",
},
)
def get_ts_info(request, ts_num):
"""
Retrieve the detailed information of a specific ts by its number.
The returned information includes ts number, title, summary, series, and series title.
"""
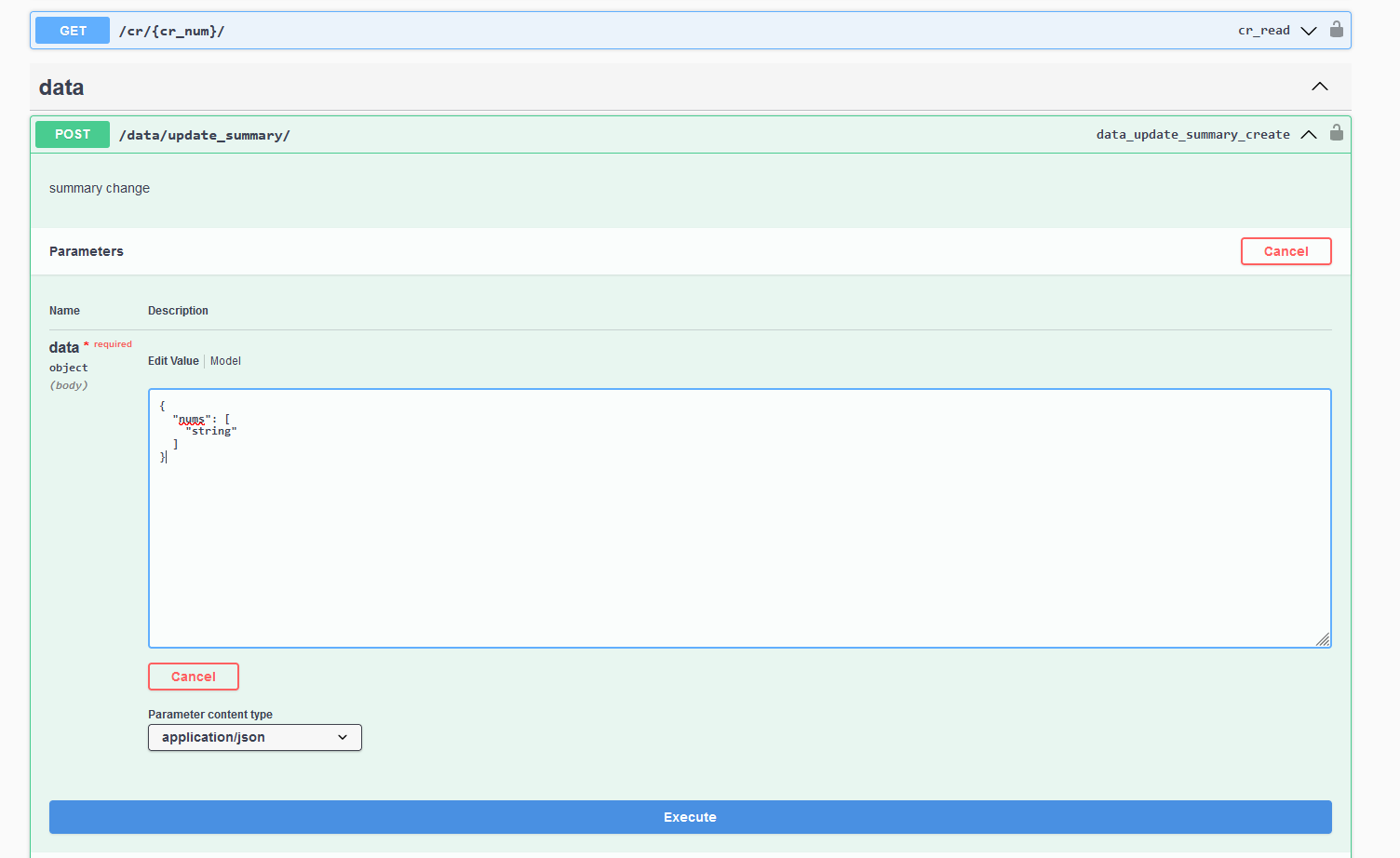
For POST method:
#FBV version
class SummaryUpdate(APIView):
@swagger_auto_schema(
request_body=openapi.Schema(
type=openapi.TYPE_OBJECT,
properties={
'nums': openapi.Schema(type=openapi.TYPE_ARRAY, items=openapi.Schema(type=openapi.TYPE_STRING),
description='[ts_num]'),
}
))
def post(self, request):
"""
summary change
"""
...
If you don’t know what’s the difference between FBV and CBV like me:
by @GPT4:
在Django REST框架中,视图可以以函数视图或类视图的形式定义。两者都可以处理HTTP请求,但是他们的使用方式、结构和优点各不相同。
函数视图(Function-based views):
函数视图是最基本的视图类型,它们是简单的Python函数,接受一个HttpRequest对象作为参数,并返回一个HttpResponse对象。例如:
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello_world(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello, World!")
你可以用@api_view装饰器来处理不同的HTTP方法。例如,处理GET和POST请求的函数视图可能如下:
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
from rest_framework.response import Response
@api_view(['GET', 'POST'])
def hello_world(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return Response({"message": "Hello, World!"})
elif request.method == 'POST':
return Response({"message": "You posted data"})
函数视图的URL配置和普通函数一样:
from django.urls import path
from .views import hello_world
urlpatterns = [
path('hello/', hello_world),
]
类视图(Class-based views):
类视图则利用面向对象的特性,允许你通过定义方法来处理不同的HTTP方法,而不是在单个函数中通过条件语句处理。例如:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
class HelloWorld(APIView):
def get(self, request):
return Response({"message": "Hello, World!"})
def post(self, request):
return Response({"message": "You posted data"})
类视图的URL配置需要使用as_view()方法:
from django.urls import path
from .views import HelloWorld
urlpatterns = [
path('hello/', HelloWorld.as_view()),
]
函数视图和类视图各有优点。函数视图通常更简单,更适合简单的逻辑。类视图可以更容易地共享公共代码并重用,它们还提供了更好的钩子和覆盖点,这对于复杂的逻辑和大型项目非常有用。
但是,无论选择哪种类型的视图,最重要的是始终保持代码清晰、简单和可维护。